Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is characterized by cancerous cells in the breast that mutate and eventually grow and spread. It can affect one breast and sometimes even both. It is a disease in which cancerous or malignant cells create a tissue mass in the breast called a tumor.
It can start in different breast parts. A breast comprises three parts:
- Lobules- These are the milk glands
- Ducts- They are the tubes for carrying milk
- Connective tissue – They consist of fatty and fibrous tissue
Breast cancer often starts in the lobules or ducts and gradually spreads outside through lymph and blood vessels. Like other types of cancers, breast cancer spreads and grows into the surrounding breast tissue and travels to other body parts. It is known as metastasized. [1]
The ICD 10 code for breast cancer is C50, categorized as a malignant neoplasm. The breast cancer ICD 10 is an international classification system for breast cancer in ICD 10 diagnosis codes list. [2]
Let’s delve deeper into the topic to learn more about breast cancer, its different types, symptoms, treatment options, and survival rate.
Types of Breast Cancer
Though breast cancer is of several types, the two most common ones are [3]:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma- The cancerous cells grow in the ducts and outside into the outer breast tissue. This type of breast cancer makes up 80 percent of the cases reported.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma: The cancerous cells start to grow in the lobules. They gradually spread to the breast tissue in the surrounding. It accounts for nearly 15 percent of the cases.
There are some special types of breast cancer. These are rare but more serious such as:
- Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive invasive breast cancer type. In this type of breast cancer, the cancerous cells don’t have ER or PR receptors (estrogen or progesterone). The cells also don’t make a protein called HER2.
- Inflammatory breast cancer is a type where the cells tend to block the lymph vessels of the skin. This blockage causes the affected breast to look inflamed.
- It is rare, accounting for 5 percent of the cases or less.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer?
Some of the early signs and symptoms of breast cancer are:
- Change in the shape, contour, and size of the affected breast
- Formation of a lump or mass in the breast
- A lump underarm that persists
- The skin of the breast and nipple feels inflamed or scaly
- Redness on the breast and nipple
- A marble-like hardened spot under the skin
- Fluid or blood discharge from the nipple
Please note that some women with breast cancer may not report any signs. That is why mammograms are routinely recommended for early detection.
Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Staging
After a patient is diagnosed with breast cancer, the doctor will determine how far it has spread, classifying it into the rights stage. In other words, the staging describes the spread of cancer in the patient's body and determines its seriousness, whether it has hormone receptors, and what may be the best way to treat it.
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed?
The doctor first performs a thorough examination of the patient's breast. After that, they will ask relevant questions like medical history, family history, and the patient's symptoms indicative of cancer. Following this, they will recommend some tests to check for abnormalities in the breast.
These tests include:
- Mammogram: It is a special test with X-ray images that help detect abnormal growth and changes in the breast.
- Ultrasonography - It uses sound waves to take pictures of the breast tissue. The results of the test help diagnose abnormalities and detect lumps in the breast.
- Positron Emission Tomography: The PET scan uses a special type of dye to highlight trigger areas. In this test, the physician injects the dye and then takes scans images via a scanner.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – The test uses radio and magnet waves for detailed and clear pictures of the structure inside the breast.
The doctor will diagnose the cancer type and stage based on the test results. If they see anything suspicious, they may even advise a breast tissue biopsy and send the sample to the pathology lab for analysis.
Breast Cancer Staging
Breast cancer can be classified into five stages. It starts from zero to four. Also, there are multiple variables in some stages. Here is a clear breakdown of the different stages of breast cancer [4]:
Stage 0: It is a pre-cancer stage. At this stage, the disease hasn’t spread out the ducts of the patient’s breast.
Stage 1-The cancerous cells start to spread gradually, affecting the tissue of the breast in the surrounding.
Stage 2: At this stage, the tumor is small (between 2 and 5cm). However, the cancer at this stage has spread to the patient’s lymph nodes or underarm.
Stage 3: Cancer spreads far from where it originated, invading nearby lymph nodes and tissue. However, the cancer still hasn’t affected the other organs. It is also referred to as the advanced stage.
Stage 4: Cancer spreads to distant body organs like the liver, lungs, brain, and bones. It is referred to as metastatic breast cancer.
Is Breast Cancer Hereditary?
Nearly five to ten percent of breast cancer cases are hereditary, resulting from mutations or changes in the gene passed on from the patient’s parent. Furthermore, T mutation inherited is also a hereditary cause of breast cancer. It can be in the BRCA2 or BRCA1 gene. Normally these genes form proteins for damaged DNA repair, but mutated versions result in abnormal growth of cells causing cancer.
Breast Cancer Survival Rate
According to the American Cancer Society, nearly 2.3 million breast cancer cases were reported in 2020. [5] It is the most common type among females.
The prognosis or survival chances vary by the stage of breast cancer. Moreover, factors like race, age, health, and how your body responds to the treatment can affect your outlook. Nonetheless, stage 0 (non-invasive) and invasive breast cancer early stage (stages 1 and 2) have a higher chance of survival than stage 3 and 4 breast cancer.
The patient has a higher survival chance if the cancerous cells are only found in the affected breast and haven’t spread or reached other parts or organs.
The lowest prognosis is among patients in stage 4 with advanced breast cancer. At this stage, cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and other body parts.
The ACS relies on data provided by SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results). NCI, or the National Cancer Institute, maintains this database. Please note that SEER doesn’t group cancer by stages. Instead, it defines them as:
- Localized – When there is no symptom or sign that cancer has spread and reached outside the breast.
- Regional – When cancer spreads outside to the lymph nodes
- Distant - When cancer spreads to different parts of the body like the liver and lungs
What Is The 5-Year Survival Rate For Breast Cancer?
The 5-year rate of survival for women in the US suffering from non-invasive breast cancer is 91 percent. Similarly, the data provided by SEER on the 5-year survival rate for a woman between 2012 and 2018 shows that women with invasive breast cancer (located only in their breast) was 99 percent.
However, the five-year survival rate of women with breast cancer that spread to their lymph nodes was 86 percent. And the five-year survival rate of women with breast cancer that reached distant body parts was 30 percent. [6]
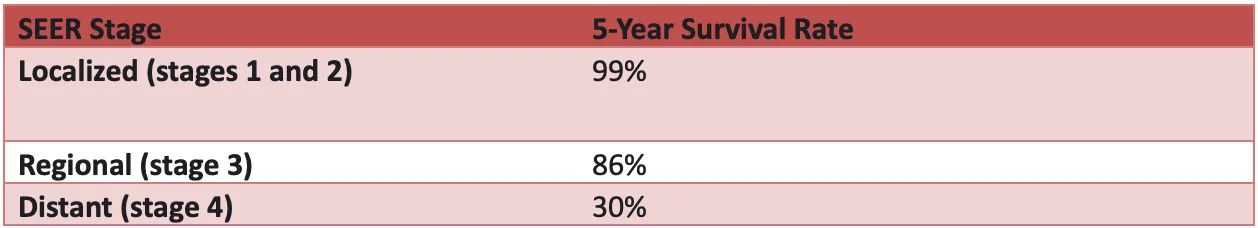
The overall survival rate varies by breast cancer stage. Women diagnosed with stage 0 to 2 breast cancer have a higher survival rate than those with stage 3 and 4 breast cancer.
Survival Rate for Inflammatory Breast Cancer
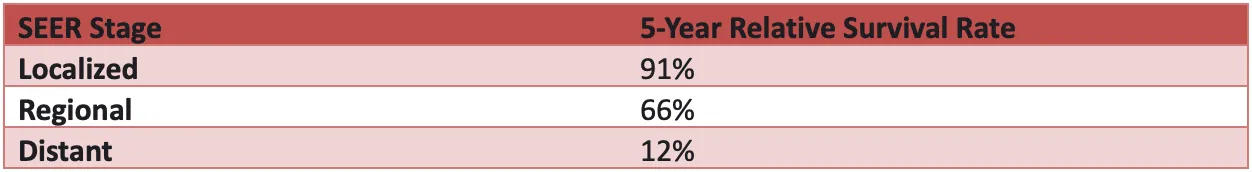
Moreover, if we look at the 5-year survival rate for inflammatory breast cancer (IBC), it is lower. This is typical because IBC grows and spreads faster. IBC is more likely to develop again even after the treatment. Hence, the survival rate is not high compared to other breast cancer types. Here’s a quick overview of the survival rate of women with IBC between 2012 and 2018:

Survival Rate for Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Like IBC, Triple Negative Breast Cancer grows fast and can develop again after the treatment. The five-year survival rate among women with Triple Negative Breast Cancer is listed below [7]:
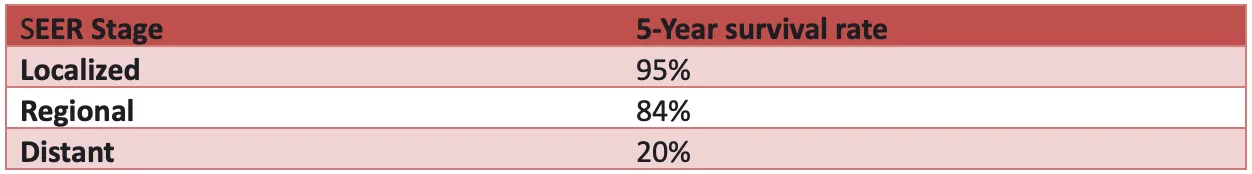
Survival Rate of Breast Cancer in Men
According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), though breast cancer in men is fairly low, it can nonetheless occur. In men, the breast cancer occurrence rate is not even one percent. Hence, men have very low chances of developing it 1/833.
But studies show that the incidence of breast cancer in men is rising. 1.2 cases/100,000 men were reported among men between 2012 and 2016 compared to 1 case/100,000 men between 1975 and 1979.
Here is an overview of the 5-year survival rate for breast cancer in men [8]:
Breast Cancer Treatment Options
The advances in medical science and clinical research breakthroughs have now made it possible for breast cancer patients to resume quality living through proper treatment. Today, multiple treatments are available for early and locally advanced stages of breast cancer.
Based on your test results and general health, the health practitioner may select the best treatment option. In general, the treatment options include [9]:
Surgery
In this procedure, the cancerous part is removed from the area surrounding it. The healthcare professional may suggest the patient surgery such as: :
Lumpectomy or partial mastectomy is a surgery that involves the removal of the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. Also, some lymph nodes may be removed for evaluation purposes. Also, the patient may undergo radiation therapy weeks following the procedure.
Mastectomy is the removal of the breast entirely. After this, some women undergo delayed or immediate breast reconstruction treatment. Furthermore, some patients may be recommended radical mastectomy if cancer spreads to the chest muscles. During the surgery, the entire breast is removed, along with underarm lymph nodes, chest wall muscles, and the nipple.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is recommended before the lumpectomy. It helps shrink the tumor. Chemotherapy is followed after surgery to detect and kill the remaining cancerous cells in the breast to lower the chances of reoccurrence.
Immunotherapy
As the name suggests, immunotherapy utilizes the patient’s immune system's power to target and attack the cancerous cells in the breast. The treatment is carried out intravenously and sometimes combined with chemotherapy.
Clinical Trials for Breast Cancer
Doctors are always searching for new, innovative, and better ways to fight and treat cancer with minimal pain and discomfort. And this is carried out through clinical research. Clinical trials are performed for all stages and types of breast cancer and focus on new treatments' efficacy and safety.
If a cancer patient is unresponsive to the standard cancer treatments mentioned above or does not want to undergo such treatments, they can join breast cancer clinical trials. There are multiple online platforms that patients and their families can use to find clinical trials for breast cancer, such as ClinicalTrials.gov and National Cancer Institute.
Conclusion
Invasive or non-invasive, breast cancer is a type of cancer that can be treated if diagnosed at the right time. Therefore, you should consult a medical practitioner if you identify any unusual changes in your breast or the signs mentioned above. As breast cancer has different stages, early detection can increase your chances of survival and improve your quality of life.