Endometrial Cancer Symptoms
What Is Endometrial Cancer?
Endometrial cancer, which is the most common type of uterine cancer, is a disease in which cancerous or malignant cells form in the lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium. Most endometrial cancers begin in the glandular cells that produce and release mucus. These are also known as adenocarcinomas [1], which make up about 80% of all endometrial cancers.
Endometrial cancer is the most common type of cancer that forms in the female reproductive system. About 50,000 Americans are diagnosed with endometrial cancer each year. [2]
Uterine cancer is of two types; endometrial cancer and uterine sarcoma. Uterine sarcoma is rare cancer but harder to treat than endometrial cancer. [3] Endometrial cancer is different from uterine sarcoma, as cancer develops in glandular cells of the uttering lining.
Endometrial cancer is grouped into one of the 4 molecular subtypes. [2]
- P53 Mutation: The overexpression of the tumor suppressor gene, p53 [4], is an important prognostic factor in endometrial cancer. The dysfunction of this gene is associated with TP53 mutation, which is detected in almost 25% of endometrial cancer cases. [5]
- POLE Mutations: Mutations in the DNA Polymerase Epsilon (POLE) occur in 10% of all endometrial cancers and result in unfavorable pathological features. [6]
- Copy Number High
- Copy Number Low
Endometrial carcinoma is divided into different histologic types based on how the cells appear under a microscope. [7] These include:
1. Adenocarcinoma: Endometrioid cancer, or adenocarcinoma, is the most common endometrial cancer. Subtypes of adenocarcinomas are;
- Adenocarcinoma has squamous cells
- Adenosquamous
- Adenoacanthoma
- Secretory carcinoma
- Villoglandular adenocarcinoma
- Ciliated carcinoma
2. Serous Carcinoma: Endometrial serous carcinoma accounts for 10% of endometrial cancers. This cancer is present in an advanced stage in older women. [8]
3. Uterine Carcinosarcoma or CS: Uterine Carcinosarcoma has the features of sarcoma and endometrial cancer. It is type 2 endometrial cancer.
4. Squamous Cell Carcinoma: It is a rare type of endometrial cancer, accounting for just 0.1% of all endometrial cancer cases. [9]
5. Small Cell Carcinoma: These are aggressive tumors with a poor prognosis and systemic spread. [10]
6. Transitional Carcinoma: It is a distinct variant of endometrial carcinoma and rare cancer.
Diagnosis and early detection of endometrial cancer depend on routine gynecology evaluations. The diagnostic tests start with a pelvic exam and a Pap test. Following the Pap test, endometrial cancer is confirmed by reviewing the results of endometrial biopsy and other important tests.
Types of Endometrial Cancer
There are 2 types of endometrial cancers; type 1 and type 2 endometrial cancer.
Type 1 Endometrial Cancer
Type 1 endometrial cancer is the most common type. They are not usually aggressive, and cancer doesn’t spread to other tissue rapidly. Type 1 endometrial cancers are mostly adenocarcinomas and are related to excess estrogen in the body. Low-grade endometrial tumors (grades 1 and 2) are included in type 1 endometrial cancers. [7] [11]
Type 2 Endometrial Cancer
Type 2 endometrial cancers are not caused by excess estrogen. Type 2 is not very common, and a small portion of endometrial cancers are included in this type. Type 2 endometrial cancers have a poorer outlook. They grow faster than type 1 cancer and are more likely to grow outside the uterus.
The serous uterine carcinomas, undifferentiated carcinoma, clear-cell carcinoma, and endometrioid carcinomas of grade 3 are included in type 2 endometrial cancer.
These cancers are higher-grade cancers as compared to type 1 and are poorly differentiated. [7] [11]
How Is Endometrial Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of endometrial cancer includes the following procedures:
Pelvic Exam
In the pelvic examination, the doctor will check for signs of abnormality around the outer genitals (vulva) and then feel the inside of the vagina and simultaneously the uterus and ovaries by placing a hand on the abdomen.
Pap Test
The Pap test, also known as the Pap smear test, involves an examination of cells obtained from the cervix under a microscope. The test helps the doctor detect abnormal changes that can lead to cancer. This test can also detect noncancerous conditions like inflammation, which means it doesn’t give a clear indication of endometrial cancer.
Endometrial Biopsy
Endometrial biopsy results show changes in cells resulting from abnormal hormone levels, polyps, or fibroids. A small flexible tube is put into the uterus to collect a sample of endometrial tissue, which is then microscopically examined.
D&C
The dilation and curettage procedure is a minor surgical procedure in which the cervix is dilated to scrape the uterine lining with a curette. The tissue from the uterus is then examined for cancerous cells. It is a more accurate procedure than biopsy to diagnose early-stage endometrial cancer patients. [12]
Transvaginal Ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound is also important for the early detection of endometrial cancer. [13] In this test, a transducer is placed in the vagina, which allows the doctor to examine the endometrium.
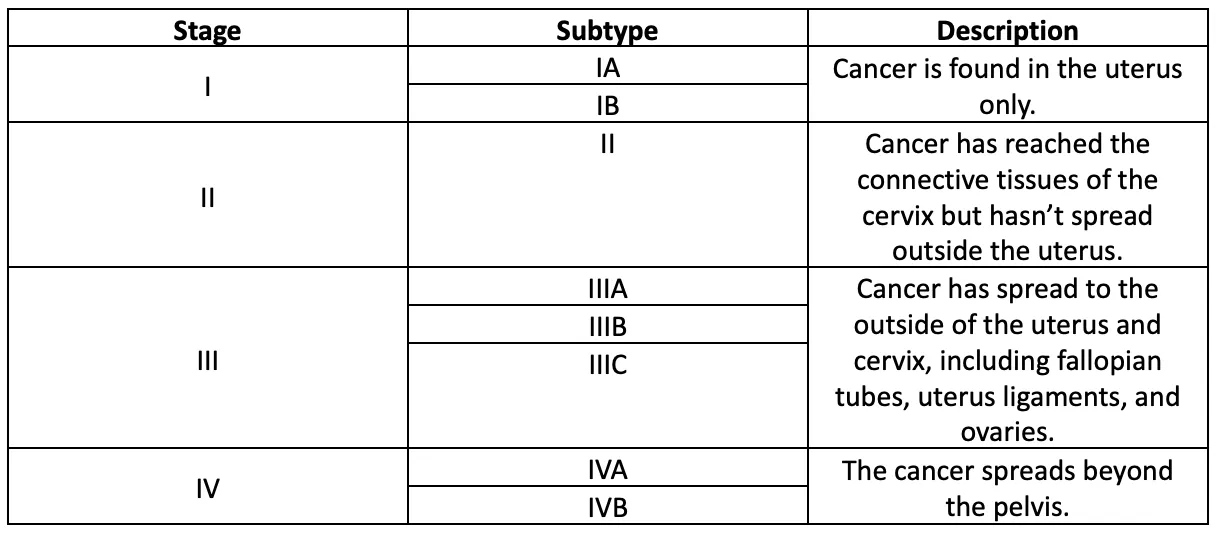
Endometrial Cancer staging
The TNM staging system classifies endometrial cancer on 3 factors:
- T: What is the size of the tumor, and how far has it grown into nearby structures?
- N: Whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M: Which defines whether cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes and organs of the body.
Endometrial cancer has the following stages:
Is Endometrial Cancer Hereditary?
Uterine cancer may run in families with hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer. These people are at a higher risk for uterine cancer. Women who have endometrial cancer should have themselves tested for Lynch syndrome, as it can have important implications for other family members. About 2 to 5 percent of endometrial cancer patients have Lynch syndrome. [14]
Endometrial Cancer Symptoms
People with endometrial cancer can experience a variety of signs and symptoms that are mostly related to the pelvic area and vaginal bleeding. If a person experiences any abnormality and changes in their body, they must immediately talk to a doctor who will suggest important tests and procedures that can identify the root of the problem.
The following signs and symptoms indicate that there is an underlying medical condition that may or may not be cancerous:
1. Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding:
Abnormal uterine bleeding includes bleeding that courses between regular monthly periods, excessive or prolonged bleeding, or extremely heavy menstruation. Possible causes for abnormal bleeding may include hormonal changes, the presence of fibroids or polyps, or uterine cancer.
2. Abnormal Pap Test Results:
Pap test results indicated changes in cells of the cervix that can be of low-grade or high-grade seriousness. A Pap smear test result can be abnormal due to vaginal or cervical infections, but the result can also indicate the presence of cancer.
3. Pain in the Pelvic Area: Pain in the pelvic area can be related to menstrual cramps, GI issues, or ovulation, but it can also indicate an infection in the female reproductive system or cancer.
What are the symptoms of Endometrial Cancer?
The most common symptoms of endometrial cancer include the following:
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
The abnormal bleeding from the vagina can range from a watery flow to heavy menstruation with lots of blood. Women with endometrial cancer have also experienced a vaginal discharge that is pink and white instead of red. Bleeding during or after the onset of menopause is also a symptom of endometrial cancer.
Abnormal Pelvic pain
Pain in the pelvic area of the body has different manifestations, which include; painful urination, heaviness or feeling of a mass in the pelvis, lower abdominal pain, and cramping below the belly. Pelvic pain can also lead to rapid weight loss.
What Are Some Signs of Endometrial Cancer?
As soon as an individual notices these alarming symptoms that could indicate endometrial cancer, it is essential to discuss the problem with the doctor, who can run helpful diagnostic tests.
Endometrial cancer signs and clinical manifestations include:
Pap Smear Test Results
The presence of cancerous or atypical endometrial cells on a Pap test is an indication of endometrial cancer. [15] Even though a Pap test alone isn’t effective in diagnosing endometrial cancer, it can screen women for cervical cancer and even find early-stage endometrial cancers.
Ultrasound Imagining Results
A thickened endometrium in patients who report post-menopausal bleeding requires further investigation for endometrial cancer diagnosis. Endometrial cancer appears as a thickening of the uterine lining that resembles a polypoid mass. The thickness of the endometrium must depend on the menstrual cycle stage of the patient. However, if the endometrium is more than 5 mm in thickness in post-menopausal women, it indicates an abnormality.
Furthermore, irregular thickening of the endometrium, intrauterine fluid collection, polypoid mass lesion, and myometrial invasion also suggest that the abnormality in sonographic features is due to endometrial carcinoma.
Symptoms of Endometrial Cancer in Women vs. Symptoms of Endometrial Cancer in Men
Endometriosis in men is an extremely is extremely rare. Uterine cancer is most common in women, and it is the fourth leading type of cancer in women in the USA1
1 Note that here, we are using the terms “women” and “men” to refer to female and male biological sex at birth, respectively.
However, recent research studies have been conducted on the effects testosterone therapy has on the reproductive organs of patients who are assigned females at birth. Recently, a 41-year-old trans man was diagnosed with invasive endometrial cancer. [16] The trans man was being examined for vaginal bleeding, and further tests revealed thickened endometrium. The biopsy provided results that indicated the presence of endometrial adenocarcinoma.
Nonetheless, the signs and symptoms that endometrial cancer produces are similar for every individual.
- Uterine cancer is more prevalent in Black women as compared to White women.
- Around 66,200 new cases of uterine cancer are expected to appear in 2023.
- The American Cancer Society also estimates that more than 13,000 women will die from uterine cancers in the USA in 2023. [17]
- Endometrial cancer is uncommon in women who are aged below 45.
Risk Factors for Endometrial Cancer
The following risk factors increase the chances of developing endometrial cancer.
- Obesity.
- Family history.
- Late menopause.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Estrogen replacement therapy.
- Infertility.
- Diabetes.
- A history of breast or ovarian cancer.
Endometrial Cancer Prevention
The prevention of endometrial cancer depends on avoiding the risk factors however possible.
Other preventative measures include:
- Using hormonal contraceptives.
- Weight loss.
- Maintaining physical health.
- Taking proper nutrition, including fruits and vegetables.
Endometrial Cancer Prognosis and Treatment
The prognosis of endometrial cancer depends on various factors that include the stage and depth of myometrial invasion, nodal status of the tumor, and lymphovascular invasion. Treatment for endometrial cancer involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. Prognosis and treatment also depend on the disease stage, histological grade, and patient’s health.
The Endometrial Cancer Survival Rate
The five-year survival rate for endometrial cancer is quite high compared to other types of cancers. The 5-year survival rate for people diagnosed with endometrial cancer is 81%. If the cancer is localized and promptly diagnosed and treated, the survival rate I seven higher.
Endometrial Cancer Treatment Options
Endometrial cancer treatment options include:
Surgery
Surgical procedures include:
- Hysterectomy
- Salpingo-oophorectomy
Radiation Therapy
Common radiation therapies for endometrial cancer include:
- External Beam Radiation
- Brachytherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy using anticancer drugs is effective in treating endometrial cancer.
Immunotherapy
Using the body’s natural immune system to fight against cancer is also an active target for research studies.
Conclusion
Takeaway
Endometrial cancer has a lot of risk factors, and most times, it cannot be prevented. But certain protective measures can decrease the chances of developing this cancer. Contacting your doctor as soon as you observe any abnormal signs in your body is essential to increase the survival rates.